Steelmaking & CCM
Perfect Fusions of Various Elements
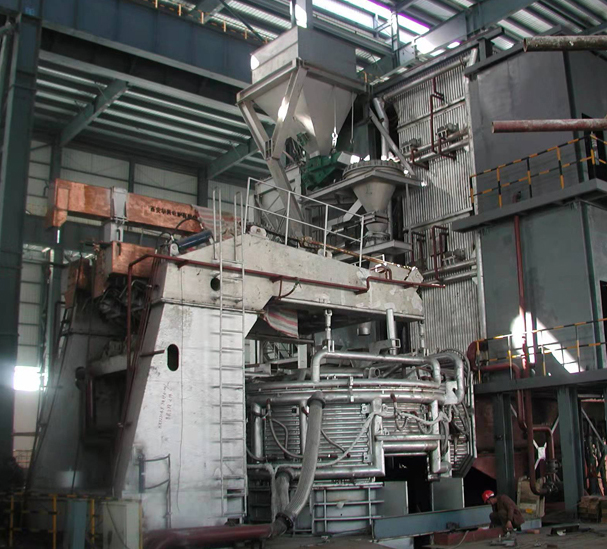
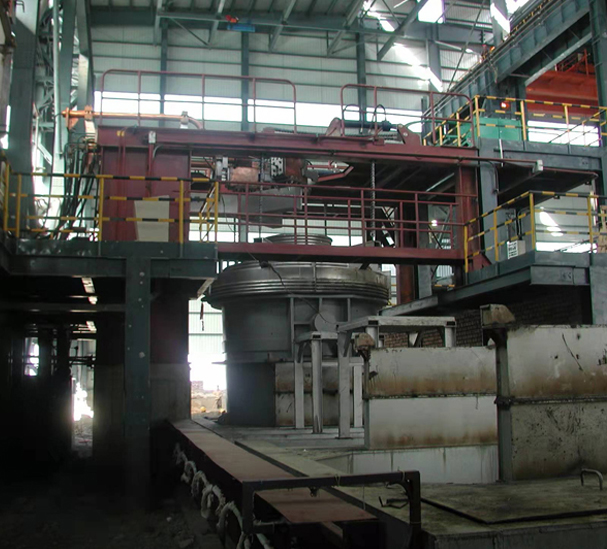
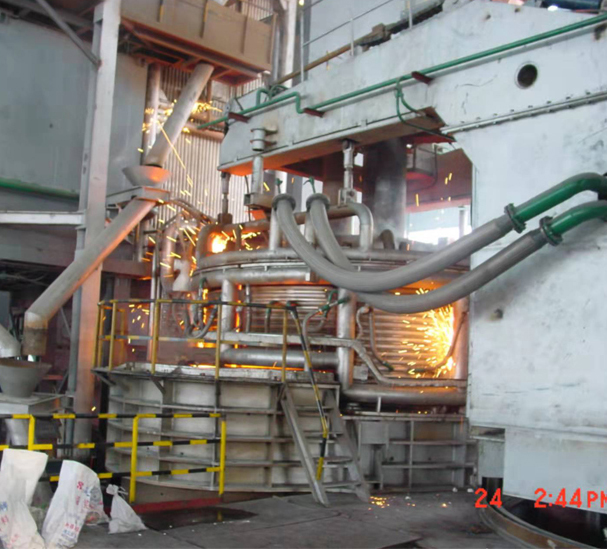
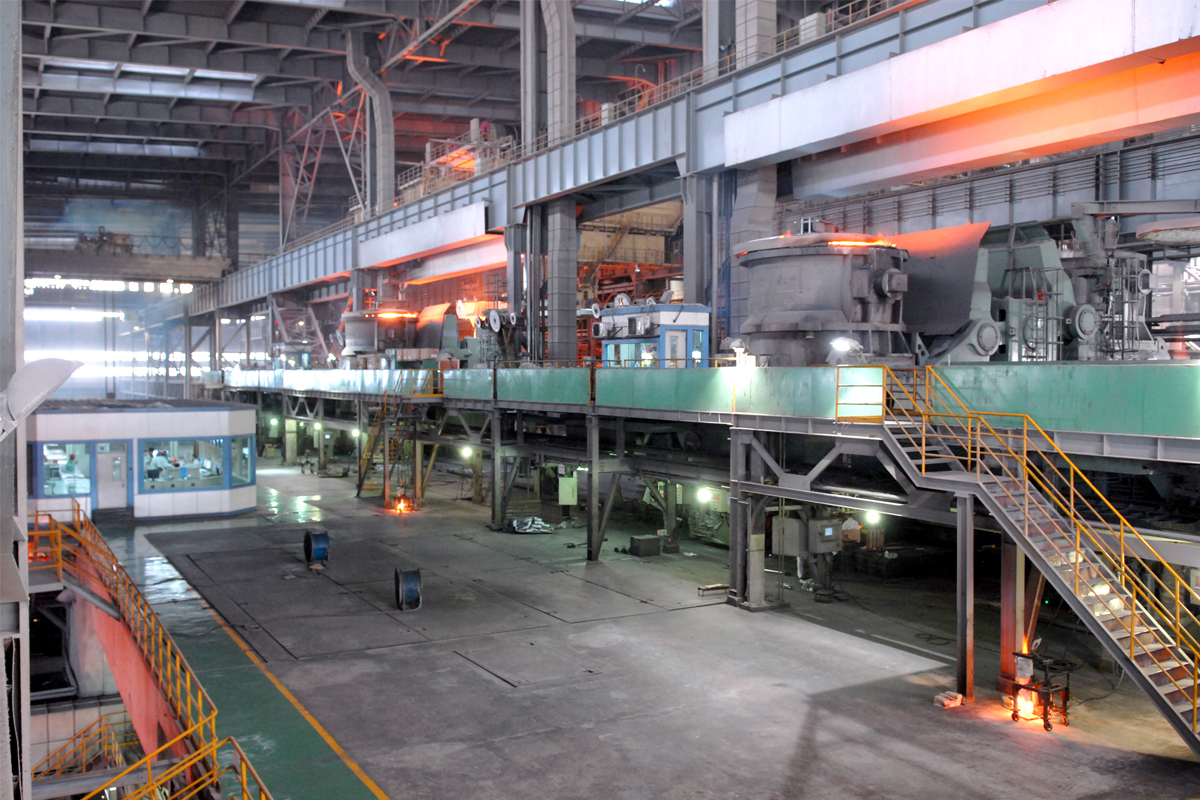
SME Group provides full set of steel making process and equipment, including electric arc furnace(EAF), medium frequency induction furnace(MIF), converter(basic oxygen furnace) steel making, ladle refining furnace, AOD, VOD, VD and related auxiliary process & equipment.

Steel is the world's most popular construction material because of its unique combination of durability, workability, and cost. It's an iron alloy that contains 0.2-2% carbon by weight.
Methods for manufacturing steel have evolved significantly since industrial production began in the late 19th century. Today, steel production makes use of recycled materials as well as traditional raw materials, such as iron ore, coal, and limestone. Two processes, basic oxygen steelmaking (BOS) and electric arc furnaces (EAF), account for virtually all steel production.
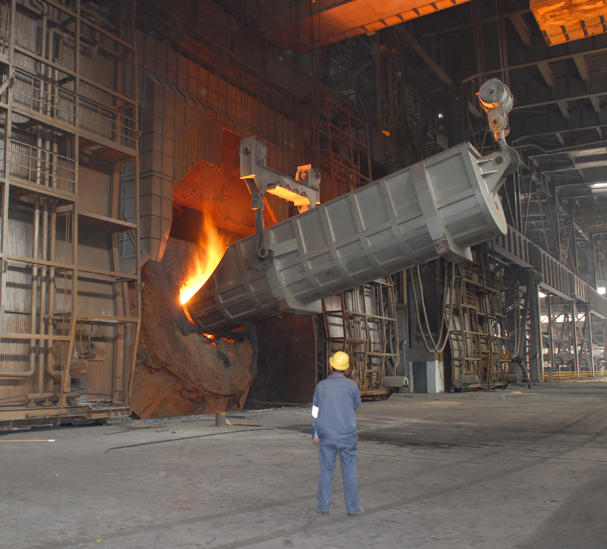
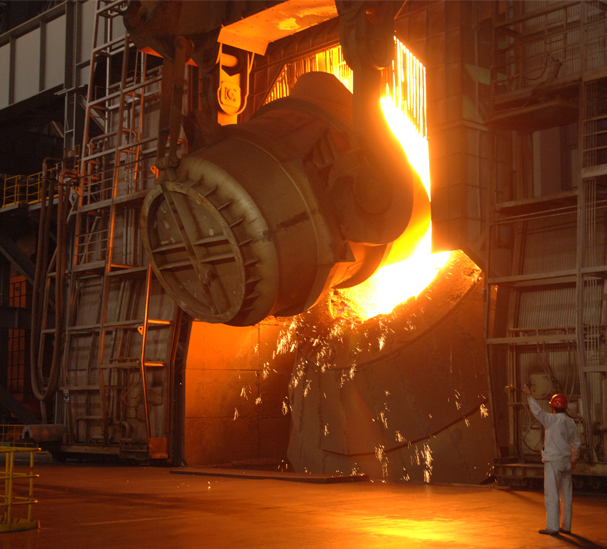
Ironmaking-the first step in making steel, involves the raw inputs of iron ore, coke, and lime being melted in a blast furnace. The resulting molten iron—also referred to as hot metal—still contains 4-4.5% carbon and other impurities that make it brittle.
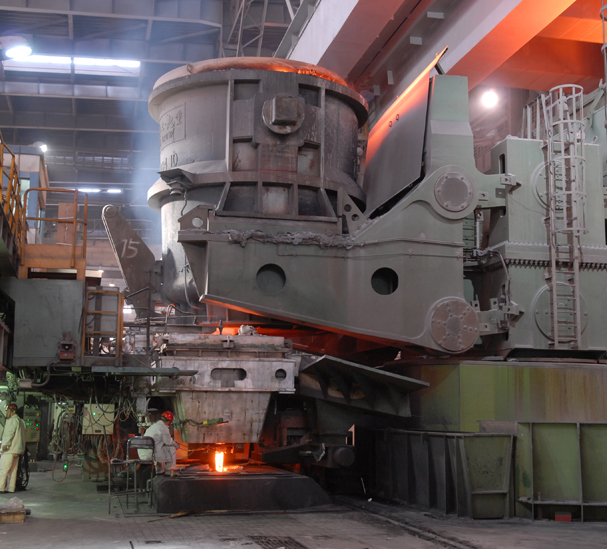
Primary steelmaking has two methods: BOF (Basic Oxygen Furnace) and the more modern EAF (Electric Arc Furnace) methods. The BOF method adds recycled scrap steel to the molten iron in a converter. At high temperatures, oxygen is blown and reacts with the carbon to generate chemical heat to melt the scrap and adjust the composition of liquid steel as rerquest, which reduces the carbon content to between 0-1.5%.
The EAF method, however, feeds recycled steel scrap through high-power electric arcs (with temperatures of up to 1,650 degrees Celsius) to melt the metal and convert it into high-quality steel.
Secondary steelmaking involves treating the molten steel produced from both BOS and EAF routes to adjust the steel composition. This is done by adding or removing certain elements and/or manipulating the temperature and production environment.
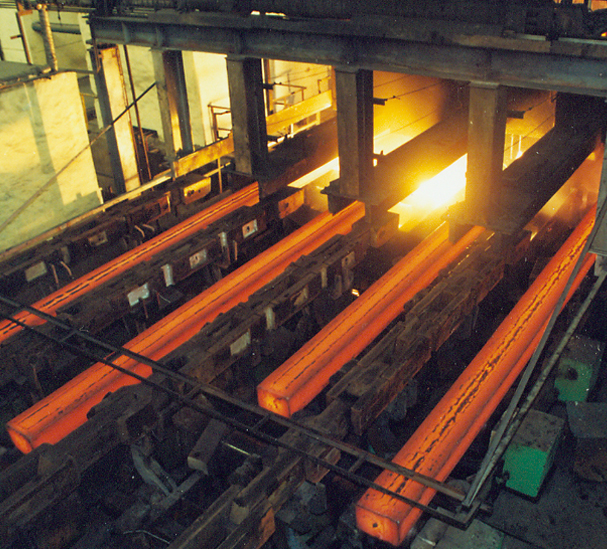
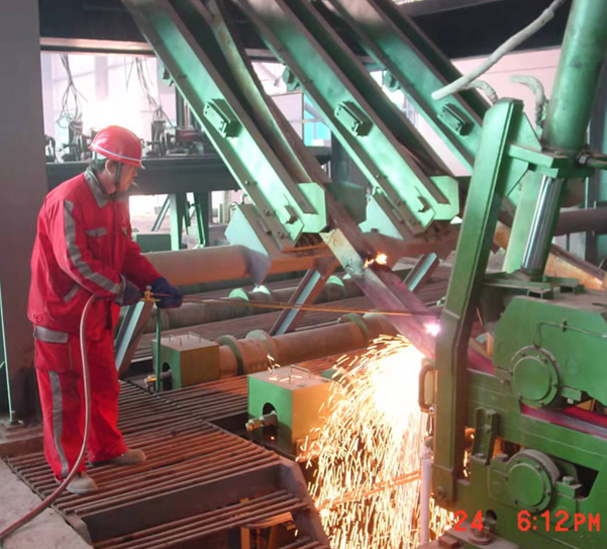
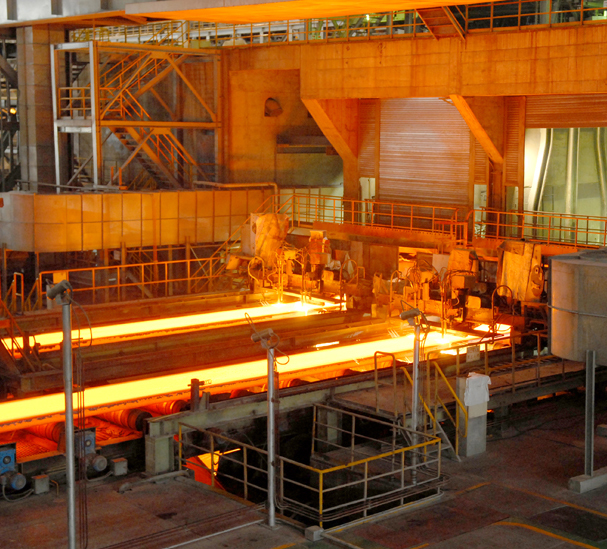
Continuous casting sees the molten steel cast into a cooled mold, causing a thin steel shell to solidify.5 The shell strand is withdrawn using guided rolls, then it's fully cooled and solidified. Next, the strand is cut depending on application—slabs for flat products (plate and strip), blooms for sections (beams), billets for long products (wires), or thin strips.
In primary forming, the steel that is cast is then formed into various shapes, often by hot rolling, a process that eliminates cast defects and achieves the required shape and surface quality. Hot rolled products are divided into flat products, long products, seamless tubes, and specialty products.
Finally, it's manufacturing, fabrication, and finishing. Secondary forming techniques give the steel its final shape and properties.
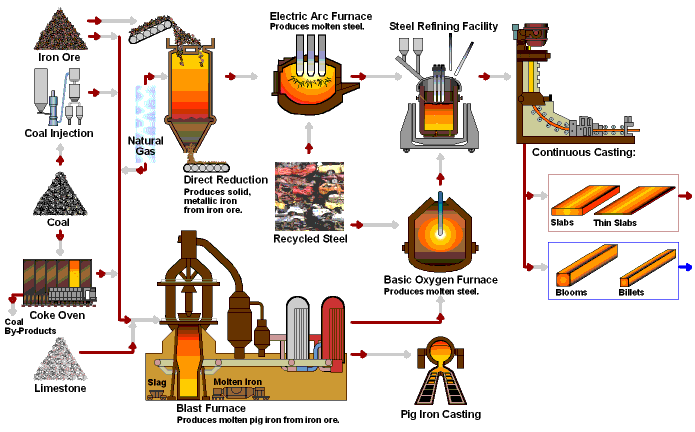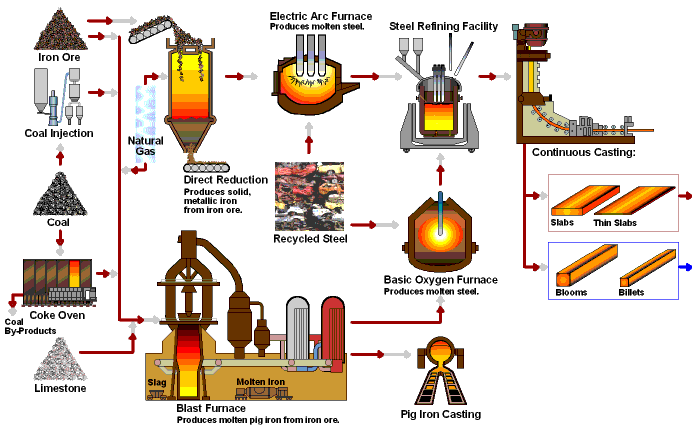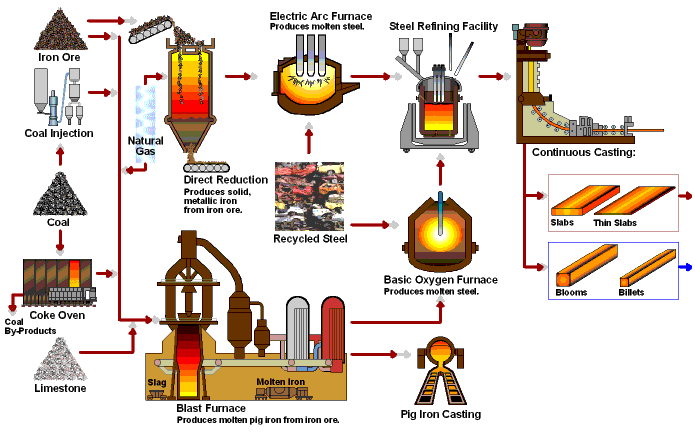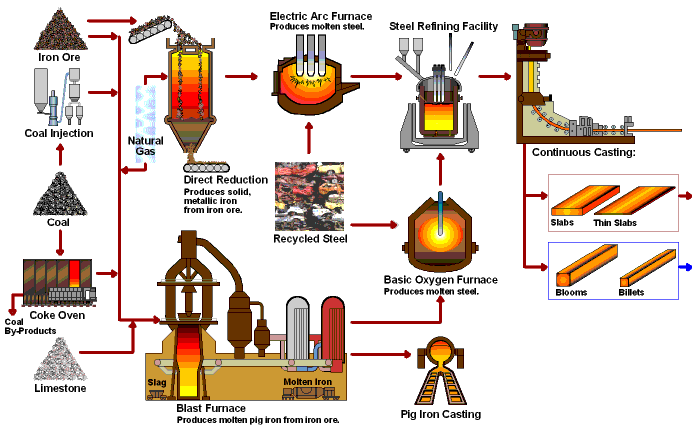
Iron and steel making process flow