Rotary Kiln
Direct Reduced Iron
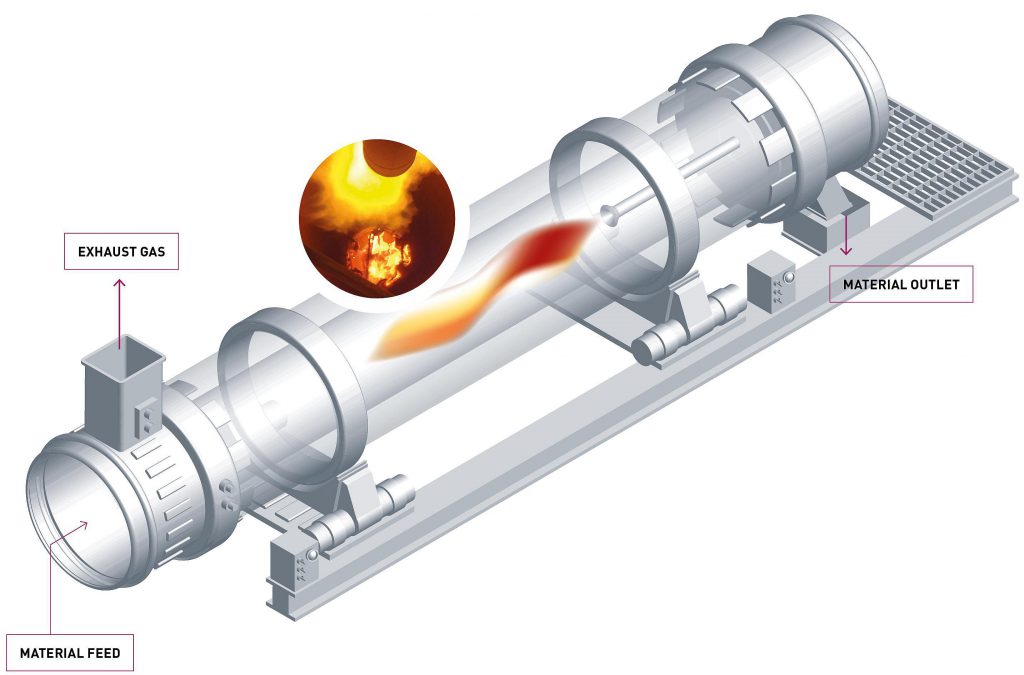
In modern direct reduction technology, the production capacity of rotary kiln direct reduction method accounts for about 20% of the world's total production capacity of direct reduction iron (DRI). Currently, there are hundreds of direct reduction rotary kilns in operation in the world. The rotary kiln direct reduction method is that the raw materials are in the rotary kiln, and the iron oxides are reduced to metallic iron under the conditions of no melting and no slag formation. The "direct reduced iron (DRI)" is commonly known as "sponge iron" because its structure is "sponge" and its bulk density is less than 2.0g/mm3.
According to the aspect ratio of the rotary kiln, the rotary kiln can be divided into:
long kiln with aspect ratio > 15, and short kiln with aspect ratio < 15.
According to whether the inner diameter of the rotary kiln changes, the rotary kiln can be divided into:
long tube kiln (straight tube kiln) and variable diameter kiln.
According to the physical and chemical reactions of the processed materials in the rotary kiln, the rotary kiln can be divided into two categories:
oxidation kiln and reduction kiln.
Oxidation kiln: The material to be treated undergoes physical and chemical reactions in the oxidizing atmosphere in the rotary kiln, such as: heating, dehydration and drying; oxidation; physical and chemical reactions such as mineral decomposition or synthesis. The free space in the rotary kiln and the material layer are in an oxidizing atmosphere.
Reduction kiln: The materials to be treated are reduced in the rotary kiln for iron minerals and nickel minerals. At the same time, according to the process requirements, physical and chemical reactions such as slagging, polymerization and growth of metal particles, and even melting can also be carried out. Ironmaking rotary kiln is the most typical reduction kiln.
The reducing rotary kiln can be divided into:
1), Preheating and pre-reduction rotary kiln: the materials in the rotary kiln are preheated, dried, crystallized water removed, carbonate decomposed, and iron minerals partially reduced. The maximum temperature in the kiln is usually ≮1000℃. Usually preheating and prereduction rotary kiln is a link in the whole process, such as: preheating prereduction rotary kiln-submerged arc furnace method to produce ferronickel.
2) Direct reduction rotary kiln: the maximum temperature of the charge in the kiln is lower than the starting softening temperature value of the material with the lowest "starting softening temperature" by 100 to 150 °C. The material in the kiln is in a completely solid state, and the reduction process is completed without melting or slag formation. The product is a "direct reduced iron" that basically retains the shape of the furnace and contains metallic iron as the main component, including the raw material gangue.
3), Deep reduction kiln
4) Particle iron rotary kiln: Particle iron method is a process method developed in Germany in the 1930s to use acid gangue ore as raw material and low-rank coal as reducing agent and fuel to produce granular metal iron. Reduction reactor for rotary kiln
5) Molten rotary kiln (pig iron cement method rotary kiln): using high alkalinity alkaline iron-containing materials as raw materials, using coal as reducing agent, the raw materials are dried, preheated, and iron minerals are reduced in the kiln , the charge will eventually form molten iron and liquid slag in the rotary kiln.