Metallurgical Process and Project Guide
The metallurgical industry can be divided into ferrous metallurgy industry and non-ferrous metallurgy industry. Ferrous metallurgy mainly refers to the production of pig iron, steel and ferroalloys (such as ferrochromium, ferromanganese, etc.), and non-ferrous metallurgy refers to the production of all other metals except the latter.
The iron and steel production process mainly includes processes such as iron making, steel making, and steel rolling, which are briefly explained as follows:
(1) Iron making: It is the process of reducing the iron in sinter and lump ore. Coke, sinter, lump ore, together with a small amount of limestone, are sent to a blast furnace to be smelted into liquid pig iron (hot metal), and then sent to a steelmaking plant as raw materials for steelmaking, or sent to a cast iron machine to be cast into pig iron blocks and stored for sale . Pig iron has a carbon content above 2%.
At present, two iron-making processes, blast furnace ironmaking and direct reduction iron, are mostly used. Among them, blast furnace ironmaking accounts for the vast majority of the world's iron production due to its low investment and high production efficiency. Coke plays the dual role of fuel and reducing agent in blast furnace smelting, which is extremely important. Blast furnace ironmaking can be operated independently or in cooperation with the steelmaking process.
(2) Steelmaking: It is to remove excess carbon, sulfur, phosphorus and other impurities in the raw materials (hot metal and scrap steel, etc.) and add an appropriate amount of alloy components. The fundamental difference between the properties of iron and steel is the carbon content, and the carbon content is less than 2% is the real "steel". What is commonly referred to as "steelmaking" is the decarburization of pig iron during the high-temperature smelting process, turning iron into steel. Commonly used steelmaking equipment is converter or electric furnace and intermediate frequency furnace. The raw materials of converter steelmaking include about 85% molten iron and 10-15% scrap steel. Then oxygen is blown into it to assist combustion, without adding any fuel, and relying on the physical heat energy of hot molten iron to make steel in a very short time. The electric furnace steelmaking relies on external energy (electricity) to heat and melt scrap steel and pig iron, and it does not use molten iron to make steel. The intermediate frequency furnace is produced in China. It smelts scrap steel through intermediate frequency induction, but the quality of molten steel is lower than that of electric arc furnace and converter, and it is generally suitable for general building materials.
(3) Continuous casting: The molten steel is continuously injected into the water-cooled crystallizer through the intermediate tank, and after solidifying into a billet, it is pulled out from the crystallizer at a stable speed, and then cooled by water spray. into a continuous casting slab of a specified length. If you do not wait for the steel billet to cool down, do not land on the way, and directly send it to the rolling mill, you can make the required steel products "in one fire". If the billet is cooled halfway and stored on the ground, the billet can become a commodity sold in the market. A small number of enterprises are more advanced and can use advanced "near-net" continuous casting methods to directly cast molten steel into very thin steel strips or billets, reducing the processing links of rolling mills, saving energy and increasing efficiency.
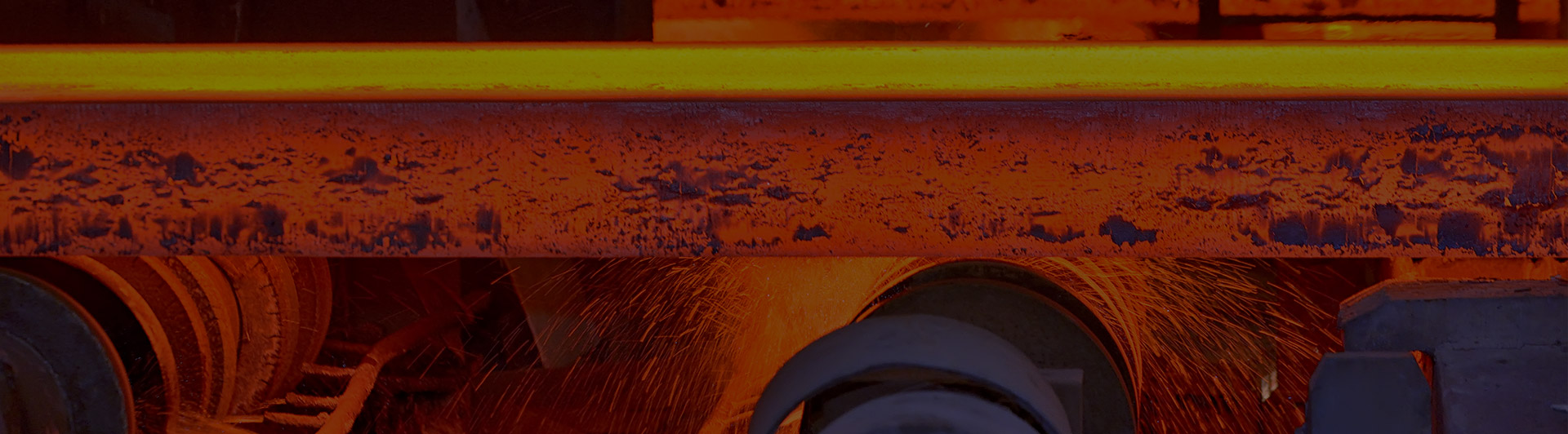
(4) Steel rolling: Continuously cast ingots and continuous casting billets are rolled into various types of steel by hot rolling or cold rolling in different rolling mills. There are many kinds of ordinary steel, and the common ones are all kinds of section steel, rebar, wire rod, steel plate, strip steel, steel pipe, etc. Some of them need hot working, some need cold working, so they all need to use rolling steel equipment, called "" rolling mill". Steel rolling is a physical change, and the billet is continuously shaped into the final product. The main steel rolling equipment includes billet heating furnace (in the case of hot steelmaking, the heating furnace is only used as a backup), rough rolling mill, intermediate rolling mill, finishing mill, and other auxiliary equipment and system. Special steel products will have corresponding equipment, such as pipe welding machines, seamless pipe equipment, etc.
Whether it is iron making, steel making or steel rolling, each stage of the process can be operated independently or in conjunction with a continuous process.